What is Uric Acid
Uric acid is a chemical product created as the result of metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides. Higher level of uric acid in blood is called Hyperuricemia. The uric acid blood test may be suggested by your doctor to identify Hyperuricemia and for gout diagnosis, gout treatments, kidney stones etc. High level of uric acid in blood causes a type of Arthritis i.e. Gout. We sometimes refer the uric acid test as gout blood test. In this article we will read in depth about what is uric acid, why we conduct the uric acid test, what are diuretic drugs effect on uric acid, overview of gout and tophaceous gout. In addition, we will also see lowering blood uric acid, use of corticosteroid, how to prepare for uric acid test and what are the high uric acid risks.
Usually the uric acid dissolves in blood and it travels to the kidneys. The kidneys then filter the uric acid and passes it out into urine. Apart from this, A small amount of uric acid also passes out of the body in your stool. However if there is too much of unic acid in your blood (Hyperuricemia), you are at risk of gout, metabolic acidosis, kidney stones and many other diseases.
High Blood Uric Acid And Purines
In addition, it may also be an indication of Diabetes, liver disease or other kidney diseases. Excessive intake of high purines foods or some other conditions may increase blood uric acid level. To clarify, Purines are nitrogen containing compounds which break down into uric acid. Few high purines foods and drinks include organ meat (such as liver, heart, brain etc), red meat, sea foods, mackerel, anchovies, dried beans, peas and alcohol. Purines form ions and salts known as urates and acid urates in blood.
Normal range of uric acid levels in healthy female is 2.4-6.0 mg/dL; and in healthy male it is 3.4-7.0 mg/dL.
You may also be interested in:
Prediabetes – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatments
Insulin Resistance – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatments
Chronic Diseases – Leading Cause of Disability and Death
Arthritis – Leading Cause of Disability
Weight Loss Diet – 12 Foods to Lose Weight Naturally
Acne Vulgaris – Most hatred Disease Among Teens
Hyperuricemia (High Blood Uric Acid) Risks
There are a number of diseases associated with consistently high blood uric acid levels. For example gout, kidney stone and other kidney diseases, toxemia in pregnancy, diabetes, kidney failure, metabolic acidosis, Lead poisoning, leukemia, alcoholism etc. Below are the most common diseases developed due to Hyperuricemia.
1. High Blood Uric Acid Causes Gout or Gout Arthritis
If the uric acid level remains high in blood it can crystallize in joints to build solid crystals within joints. This situation causes the severe joint pain and called Gout or Gout Arthritis. Gout treatment requires to lower your uric acid along with other medications. In Addition, if the high level of uric acid remains untreated, these uric acid crystals can grow up in the joints and nearby tissues to form hard lump deposits called tophi.
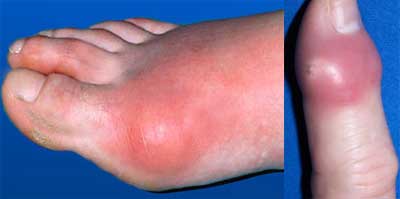
Though the tophi are most commonly found as hard nodules around the fingers, at the tips of the elbows, and around the big toe, but they could appear anywhere in the body. If we do not treat Gout at initial stage, it may become a Chronic disease. Tophaceous Gout is the chronic form of Gout. High levels of uric acid may also cause kidney stones or sometimes kidney failure.
2. High Blood Uric Acid Causes Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a condition occurred due to high level of uric acid in blood. The symptoms of metabolic acidosis include rapid breathing accompanied by confusion and lethargy. This may sometimes lead to shock and death of the person. Sometimes, if a person with high uric acid eats proteins in high quantity, it may not be metabolized properly. This may result in over production of uric acid in the blood and lead to metabolic acidosis attack.
3. High Blood Uric Acid Can Cause Kidney Stones

High level of uric acid may lead the uric acid to crystallize in kidneys. This crystallization of uric acid forms various sized stones in kidneys. These stones stuck in the ureters while the patient attempts to urinate. As a result, this condition causes the severe pain in kidneys and may lead to several other kidney disease. If you are high on uric acid, you may need to eliminate the foods having high level of purines (cause of uric acid formation) form your meal such as organ meat and animal protein etc. This may reduce risk of developing kidney stones.
4. High Blood Uric Acid Can Cause Heart Failure
Some latest researches has shown that high uric acid may increase the risk of heart failure, overtime. “Our study shows that high levels of uric acid significantly increase your risk of developing heart failure later in life,” said Dr. Eswar Krishnan, MD, assistant professor of immunology and rheumatology. Dr. Krishnan has received grant support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals of North America Inc. of Deerfield, Ill., (formerly TAP Pharmaceutical Products, Inc.) and previously held stock in Savient Pharmaceuticals.
Causes of High Blood Uric Acid (Hyperuricemia)
We can classify the causes of Hyperuricemia into two categories i.e. Primary Hyperuricemia and Secondary Hyperuricemia.
A. Primary Hyperuricemia
If the uric acid level is increased due to purines, this is called Primary Hyperuricemia. Eating foods very high in purines can cause the increased level of purines in our body and thus causing primary hyperuricemia. Below is the list foods with high and low purines:
Foods High in Purines
- All organ meats (such as liver, brain, heart), meat extracts and gravy.
- Some sea foods such as sardines, herring and scallops.
- Red meats such as beef or lamb.
- Yeasts and yeast extracts (such as beer, and alcoholic beverages)
- Alcohol
- Avoid Diuretic drugs and medications such as thiazide diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide), and loop diuretics (such as furosemide or Lasix®). Diuretic drugs may increase the production of purines which will cause productions of more uric acid.
Foods that are low in purines include:
- Drink enough water and keep yourself hydrated.
- Milk and other milk products.
- Fruits, Asparagus, Lettuce and other green vegetables
- Eggs, Nuts and Peanut butter
- Refined cereals like breads, pasta and tapioca
- These vegetables (Asparagus, spinach, beans, peas, lentils, oatmeal, cauliflower and mushrooms) are also high in purines. However as per researches, vegetables high in purines are not that much harmful as of purines from meat and alcohol. So these vegetables are safe to take in moderate quantity.
B. Secondary Hyperuricemia
If the increase blood uric acid level is due to any other disease or conditions other than purines breakdown, then we call it Secondary Hyperuricemia. And here are some possible conditions which can increase your uric acid level.
- Cancers or chemotherapy agents – Chemotherapy destroys the cancer cells. This process may release uric acid into blood and causes the secondary hyperuricemia.
- Kidney Diseases – If due to certain kidney disease your kidneys are not functioning well and the kidneys are not able to move the excess uric acid out from your blood into urine.
- Long fasting, starvation and malnutrition
- Certain Medications – There are some certain medications which can cause increased levels of blood uric acid. For example Coumadin, some diuretics, lower doses of aspirin (75 to 100 mg daily), niacin, cyclosporine, vitamin C (ascorbic acid), levodopa and some other medicines which Doctors use to treat tuberculosis, leukemia and lymphoma.
- Metabolic Disorder Related Disease such as Diabetes or Acidosis
- Lead poisoning
Treatments and Medications for Hyperuricemia
We strictly recommend that any medication must be taken under the prescription of your doctor only. Based on your disease conditions, your doctor may suggest medications to treat high uric acid levels. Few of the medications may include:
1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) agents and Tylenol®
Medicines such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium may provide relief from pain of Gout. Gout is a type of arthritis developed as a result of crystallization of uric acid in joints.
2. Acetaminophen
If NSAID drugs are not recommended for you due to certain types of cancer or chemotherapy, your doctor may suggest you the limited dosage of Acetaminophen. Do not increase the medication more than recommended by your doctor as it may cause liver damage.
3. Uricosuric Drugs
Drugs like Uricosuric drugs including probenecid, and sulfinpyrazone help preventing uric acid crystals from being deposited into your tissues.
How Blood Uric Acid Test is Performed
As the name suggests, the physician performs blood uric test by taking blood sample usually from the vein located on inside of elbow or the back of the hand. The physician taking blood sample will belt an elastic rubber band around your upper arm. This will stop blood flow to and from your hand. This makes the vein in your arm little blown up and more visible so that blood sample could be taken easily.
Then when the vein is visible clearly, the physician will clean the point with spirit or alcohol and draw blood with the help of a needle and injection.
The collected blood sample is then sent to lab for blood uric acid measurement.
Why Blood Uric Acid Test is Performed
There are several diseases and conditions associated with the low or high uric acid. To diagnose these diseases your doctor may want to look at your uric acid measurements.
1. Joint Pain or Gout Arthritis
High level of uric acid (hyperuricemia) leads to produce one of the most painful diseases i.e. Gout. To diagnose gout arthritis, a blood uric acid test is required. Gout treatment process will first require to lower uric acid so that no further crystallization of uric acid happens in joints. As the prime reason of gout arthritis is high uric acid, sometimes we refer blood uric test as the gout blood test.
2. Kidney Stones
Increased blood uric (hyperuricemia) acid is also responsible to develop kidney stones and a uric acid test is required in patients with kidney stones. This helps the doctor to plan your medications accordingly.
3. Check Performance of Uric Acid Lowering Medicine
If you are undergoing gout treatments or treatment of any other disease which require to lower the uric acid, your doctor may want to check if the medicine are really working.
4. Chemotherapy or Radiation Treatments
If a person is to undergo Chemotherapy or Radiation therapy which is done to destroy cancer cells, this process can release the uric acid into blood. This process may also require to check your blood uric acid measurements.
5. Find Kidney Disorders
Kidneys are responsible in your body to filter out uric acid from your body into urine. If your uric acid is high, your kidney may not be functioning properly. A blood uric test will help to find out any possible kidney disorders.
Prepare for Blood Uric Acid Test
Uric acid test require you to be empty stomach since 4 hours before the test is performed. There are some other conditions too which could influence the test results.
- Consumption of Alcohol
- Many medicines can interfere in results of uric acid test such as aspirin and ibuprofen (Motrin) etc. Tell your doctor if you are taking these or any other medicine before the blood uric test.
- Increased vitamin C can also influence the results.
- Dyes used in X-ray tests can also affect the blod uric acid test results.
Blood Uric Acid Test Results
The amount of uric acid in blood is measured by the uric acid test. The lab reports are usually available within a day or two.
The reference range of normal blood uric acid may have little variations in different labs and your lab report must have the reference range mentioned on it. Rest your doctor may evaluate your uric acid results based on your health and other factors.
Here is the most widely accepted normal range of uric acid for men, women and children.
Men – The normal blood uric acid range in a healthy men is 3.4 mg/dL to 7.0 mg/dL (202 mcmol/L to 416 mcmol/L)
Women – The normal uric acid range in a healthy women is 2.4 mg/dL to 6.0 mg/dL (143 mcmol/L to 357 mcmol/L)
Children – The normal uric acid range in a healthy child is 2.0 mg/dL to 5.5 mg/dL (119 mcmol/L to 327 mcmol/L)